Performance and rendering
Row virtualization is a performance optimization technique used in Grid. Instead of rendering all the rows of data at once, which can be thousands of entries, row virtualization renders only the rows currently visible within the user’s viewport (plus a small buffer). As the user scrolls, the Grid dynamically renders new rows and removes those that scroll out of view.
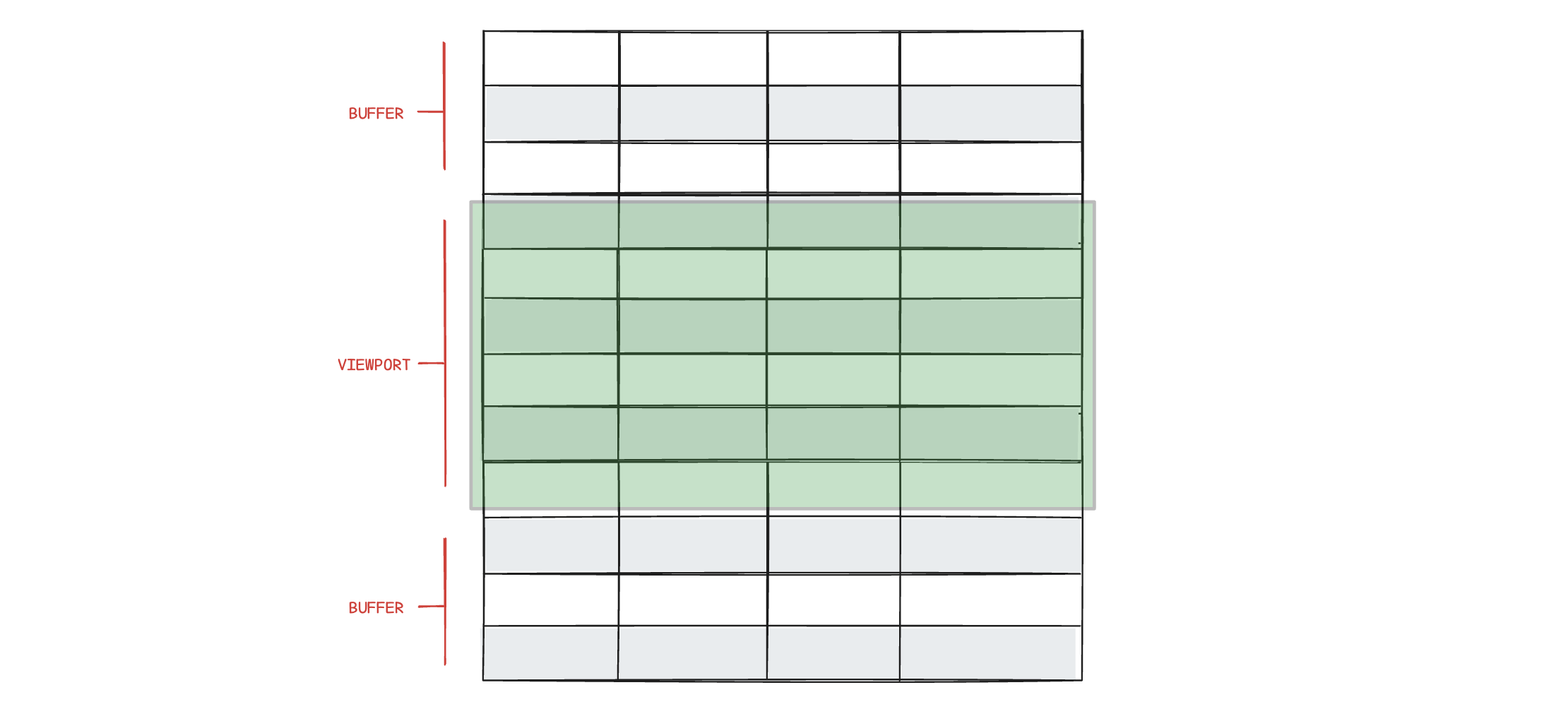
This technique significantly enhances performance, leading to faster load times and efficient updates. Row virtualization reduces memory consumption, allowing the application to handle large datasets smoothly without compromising performance. Users benefit from a smoother experience with fluid scrolling and more responsive interactions such as sorting rows.
The row virtualization is enabled by default; however, you can easily disable it using the virtualization option.
Please note that large datasets also impact resizing and sorting performance. Some animations or interactions might not be smooth.
Optimizing performance
{
rendering: {
rows: {
bufferSize: 3, // default is 10
strictHeights: true // default is false
}
}
}The bufferSize and strictHeights options can be adjusted to optimize performance and smoothness of scrolling based on your specific use case and preferences.
buffersize
Defines the number of rows rendered outside the viewport (the buffer) during scrolling. A small buffer leads to faster initial rendering and increased performance on sorting and scrolling. A larger buffer means slower initial rendering but might decrease the flicker effect on fast scrolling.
The default bufferSize of 10 should be optimal in most cases.
strictHeights
By default, rows adjust their height to fit all content, which can reduce performance and scrolling smoothness. Setting strictHeights: true ensures all rows have a uniform height, truncating multiline text with an ellipsis. This skips height calculations and boosts performance.
Rendering
{
rendering: {
table: {
className: "custom_table_class"
},
header: {
enabled: false // default is true
},
columns: {
resizing: {
mode: "fixed"
}
}
}
}These options can be used to configure how the table should be rendered.
table.className is appended to the <table> element.
header.enabled: false disables all column headers by not rendering the thead element.
columns.resizing.mode is used to configure initial column widths.
columns.resizing.mode: "full" renders a full width (width: 100%;) responsive table with evenly distributed column widths. columns.resizing.mode: "fixed" renders a table were columns have a fixed width in pixels. It should be set to support your specific use case.